10 Network Troubleshooting Commands for MacOS
A Guide to networking commands on MacOS

Image created with the use of A.I.
Researching network issues on MacOS can seem like an overwhelming task. MacOS offers an array of tools that can help simplify this task. This article takes a look at ten terminal commands that can be used to troubleshoot network issues on MacOS. We recommend bookmarking this article on IPSearch.io as well as bookmarking in your browser.
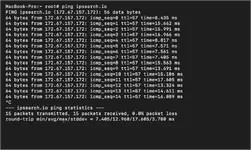
The
Read more: Understanding the Ping Command
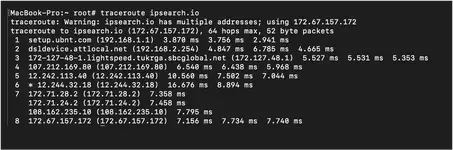
The
Read more: Using the Traceroute Command
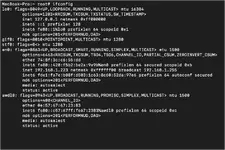
The
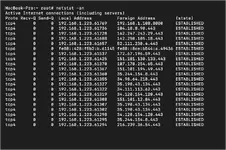
The
The
The
The
The
The
The
if you have any questions or commands about this article then please leave a comment or post in our forums.
1) ping
Command:ping [destination]
The
ping command uses ICMP packets to test the connectivity from your computer to a destination host. You can either ping an IP directly or ping a domain name. If a ping fails between your computer and a destination then the destination is unreachable and it is recommended to perform a traceroute to see what hop the request failing.Read more: Understanding the Ping Command
2) traceroute
Command:traceroute [destination]
The
traceroute command is used to diagnose where delays may occur when communication with a host. When you make a request to a IP or domain, your request is routed through different nodes before it reaches the destination. For example, if IPSearch.io is slow to load then conducting a traceroute against the domain will show you where in the route the delay occurs.Read more: Using the Traceroute Command
3) ifconfig
Command:ifconfig
The
ifconfig command shows all of your network interfaces, which ones are active, and the IP address for each. In the example above you can see that my private IP address is 192.168.1.223.4) netstat -an
Command:netstat -an
The
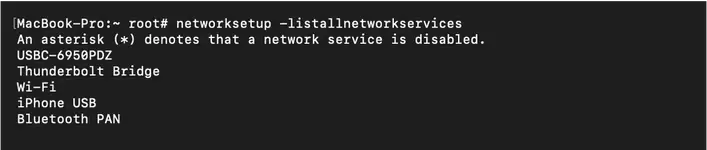
netstat -an command displays IP addresses your computer is currently connected to. This results could be websites or any other service your computer is connected to.5) networksetup -listallnetworkservices
Command:networksetup -listallnetworkservices
The
networksetup -listallnetworkservices command displays the services on your computer that are available to use to connect to another network.6) scutil --dns
Command:scutil --dns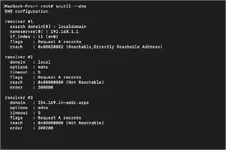
The scutil --dns command shows DNS configuration information. This command is helpful if domains are not resolving and you have a specific DNS server use.7) dig
Command:dig [domain]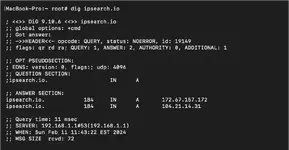
The dig command retrieves DNS information for a specific domain. In the example above, you can see the two "A" records for IPSeaerch.io. This tool is helpful is validating an update to DNS settings on a domain is being used by the DNS server your ISP uses.8) nslookup
Command:nslookup [domain]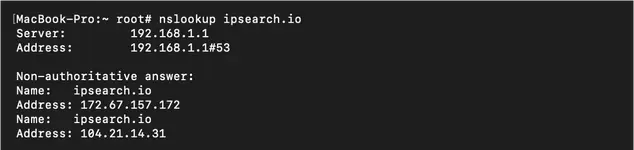
The nslookup command is similar to dig in that it returns DNS "A" records for a specific domain. The nslookup command also returns the current server / router your computer is connected to.9) arp -a
Command:arp -a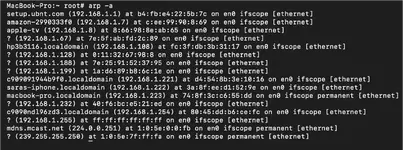
The arp -a command displays the IP address and MAC (physical) addresses of the devices your computer is connected to on the network. This command is helpful in understanding what physical device is associated with an IP address.10) route -n get default
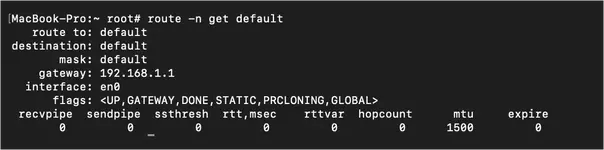
Command:route -n get default
The
route -n get default shows the default route your computer takes when communicating with other devices or websites. This command is helpful if multiple computers on the same network are experiencing different results when connected to another device, service, or website.Conclusion
These commands represent a good starting point when troubleshooting issues or testing the performance of a MacOS devices on a network. Several of these commands have other options and in the future we will dig deeper into each command and update this article with a link to the deep dive.if you have any questions or commands about this article then please leave a comment or post in our forums.

